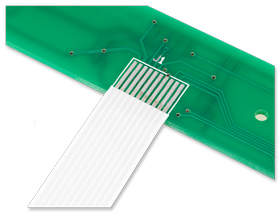
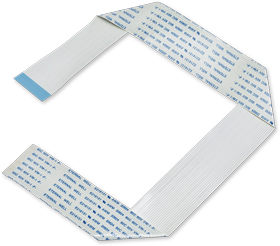
Flat Flex
Flat flex cables are light weight, low profile, small outline cables designed to satisfy high density cabling applications. Their distinguishing factors include repeated dynamic flexing and the ability to fold into nearly any shape, evenly distributing stress especially when compared to traditional cabling.
Flat flex cables can be designed to hold any number of electrical components or simply as a connector between two circuits. Common industry applications include, but are not limited to: consumer electronics, telecommunications, medical, automotive, industrial and commercial.

Flexible Circuit Technologies, a premier global supplier in design and production of
Flexible Circuits, Rigid Flex, Flexible Heaters, Flat Flex Cables, Membrane Switches, Plastic Moldings, Assemblies, Product Module Builds to Complete Product Box Builds
For more in depth information on Flat Flex, click on the links below:
In summary, if you have flexible circuit design or flexible printed circuit board needs, we can help.